Being a vegetarian doesn’t mean compromising on nutrition or flavor. With a thoughtful approach and a variety of plant-based foods, vegetarians can enjoy a balanced and satisfying diet.
When it comes to meeting your nutritional needs as a vegetarian, ensuring an adequate intake of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats is essential. Fortunately, there is an abundance of plant-based options that can provide all three macronutrients, allowing you to thrive on a well-balanced vegetarian diet. In this blog post, I will explore various sources of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to help you create a diverse and nutritious meal plan.
Protein Powerhouses for Vegetarians
While animal products are traditionally known for their protein content, vegetarians have numerous plant-based options to choose from. Incorporate the following protein-rich foods into your diet
- Legumes and Pulses: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and soybeans are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and various minerals. Include them in soups, stews, salads, and veggie burgers.
- Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based products are versatile and can be used in stir-fries, curries, or marinated and grilled for a protein-packed main dish.
- Quinoa: Considered a complete protein, quinoa is a seed that can be enjoyed as a side dish, in salads, or as a base for grain bowls.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and hemp seeds are not only rich in protein but also provide healthy fats. Sprinkle them on salads, or yogurt, or blend them into smoothies for an added protein boost.

Carbohydrates for Sustained Energy
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy, and as a vegetarian, you can enjoy a wide range of healthy carbohydrate-rich foods. Incorporate the following into your meals
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat bread, and pasta. They provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals along with complex carbohydrates.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These natural sources of carbohydrates also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Enjoy a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables as part of your daily diet.
- Sweet Potatoes and Legumes: Sweet potatoes are a nutritious carbohydrate source, while legumes like chickpeas and kidney beans offer a combination of protein and carbohydrates.

Healthy Fats for Optimal Health
Vegetarians can obtain healthy fats from various plant-based sources. Include the following options in your diet
- Avocados: Loaded with monounsaturated fats, avocados are not only creamy and delicious but also provide important nutrients like vitamin E and fiber.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants. Enjoy them as snacks or add them to your meals.
- Olive Oil and Coconut Oil: These oils can be used for cooking and dressing salads, providing healthy fats and adding flavor to your dishes.

A well-planned vegetarian diet can provide an abundance of macro and micronutrients necessary for optimal health. By diversifying your food choices and incorporating a variety of plant-based sources, you can ensure you’re meeting your body’s needs. I will delve into the world of macro and micronutrients, highlighting their importance and suggesting vegetarian-friendly options to include in your diet.
Macronutrients for Energy and Vital Functions:
- Carbohydrates: As the primary source of energy, carbohydrates should make up a significant portion of your daily caloric intake. Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. Additionally, include fruits, vegetables, and legumes for their fiber content and array of beneficial nutrients.
- Proteins: Essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues, proteins can be obtained from various plant-based sources. Include legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, along with soy products like tofu and tempeh. Nuts, seeds, and whole grains like quinoa also contribute to your protein needs.
- Healthy Fats: Fats play a crucial role in providing energy, supporting cell function, and aiding nutrient absorption. Opt for sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and coconut oil. These provide monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 fatty acids.
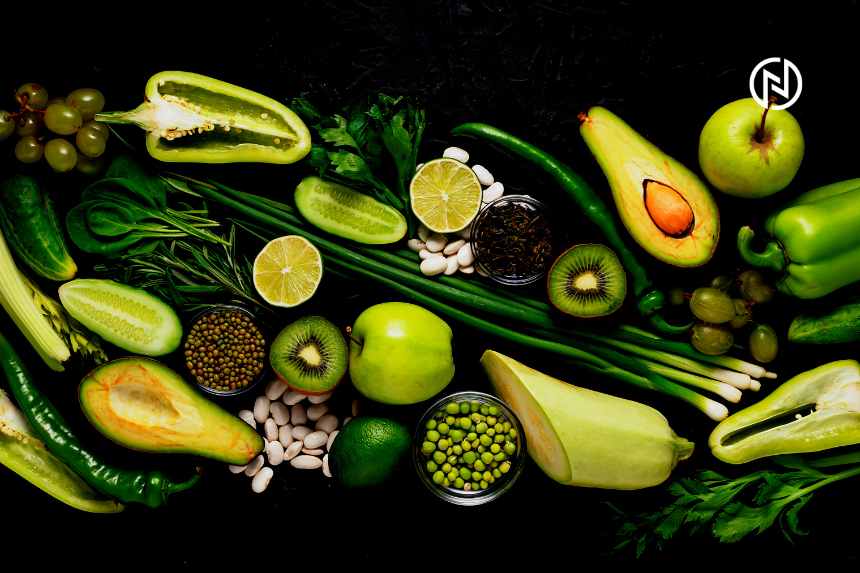

Micronutrients for Optimal Health:
- Vitamins: Vegetarians have plenty of options to obtain essential vitamins. Include a variety of fruits and vegetables to ensure an adequate intake of vitamins A, C, E, and K. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale, citrus fruits, and berries are excellent choices.
- Minerals: Plant-based sources can fulfill your mineral requirements. Leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and seeds are rich in iron, magnesium, zinc, and calcium. Include fortified plant-based milk alternatives or calcium-set tofu for additional calcium.
- Antioxidants: Colorful fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants that protect against cell damage and support overall health. Berries, tomatoes, bell peppers, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are great choices.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Incorporate flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts into your diet for plant-based omega-3 fatty acids. These provide numerous health benefits, including supporting brain function and reducing inflammation.
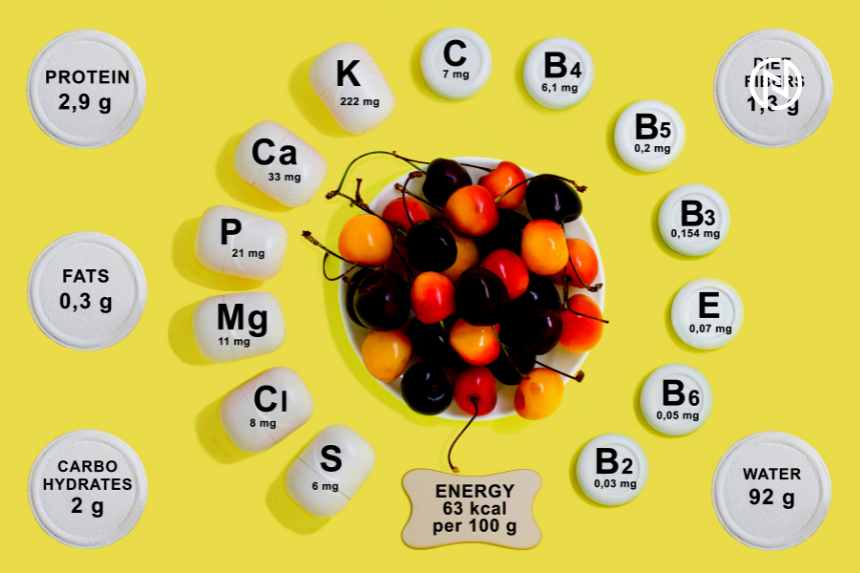
Here is a comprehensive list of vegetarian foods along with their nutritional facts
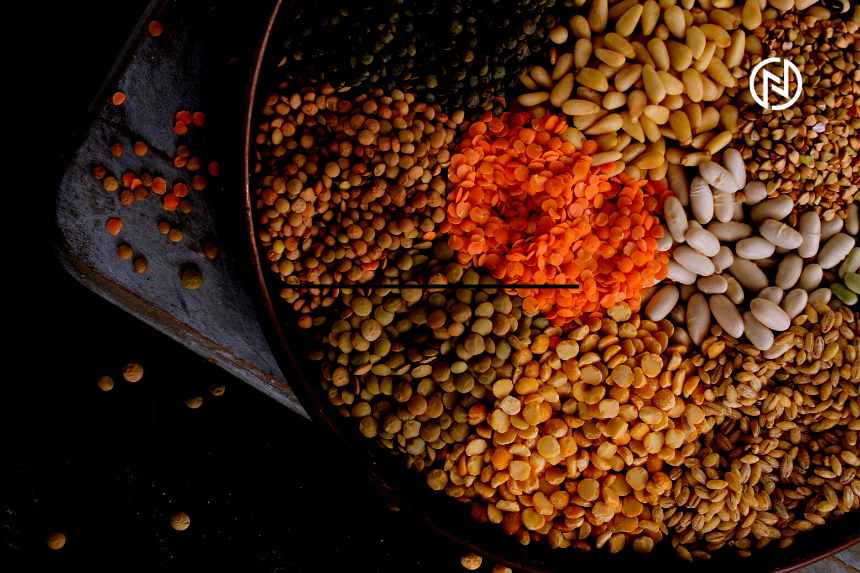
Legumes and Pulses
- Lentils: Rich in protein, fiber, iron, and folate.
- Chickpeas: High in protein, fiber, iron, and vitamin B6.
- Black beans: Excellent source of protein, fiber, iron, and magnesium.
- Kidney beans: Packed with protein, fiber, iron, and potassium.

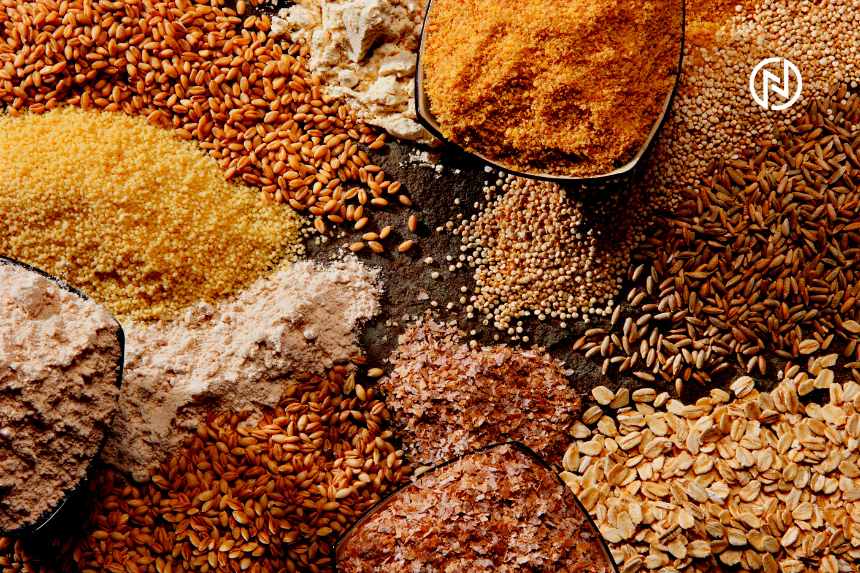
Grains
- Quinoa: Contains complete protein, fiber, iron, and magnesium.
- Brown rice: Good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and B vitamins.
- Oats: High in fiber, protein, and various minerals.

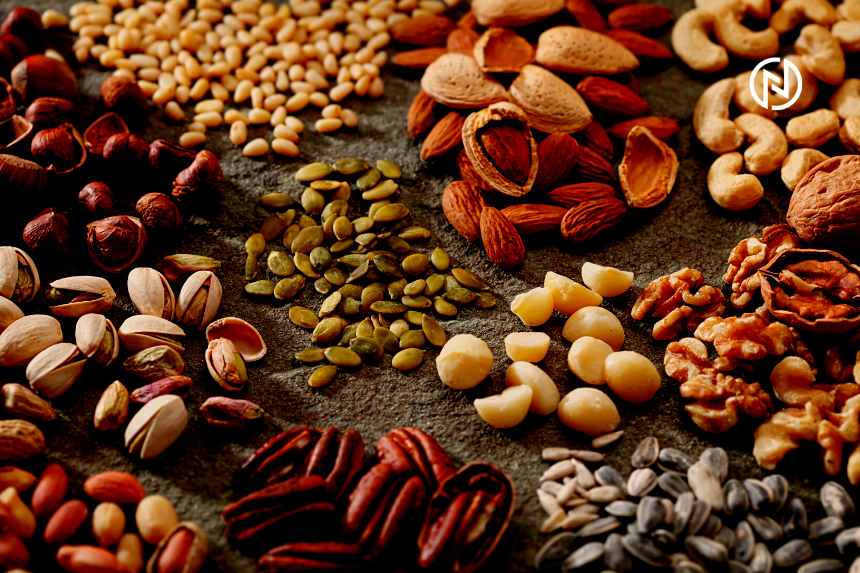
Nuts and Seeds
- Almonds: Rich in healthy fats, protein, vitamin E, and magnesium.
- Walnuts: Good source of omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and antioxidants.
- Chia seeds: High in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and calcium.
- Flaxseeds: Packed with omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and lignans.

Dairy Alternatives
- Soy milk: Provides protein, calcium, and vitamin D.
- Almond milk: Low in calories, high in vitamin E, and fortified with calcium.
- Coconut milk: Creamy and rich in healthy fats, iron, and magnesium.

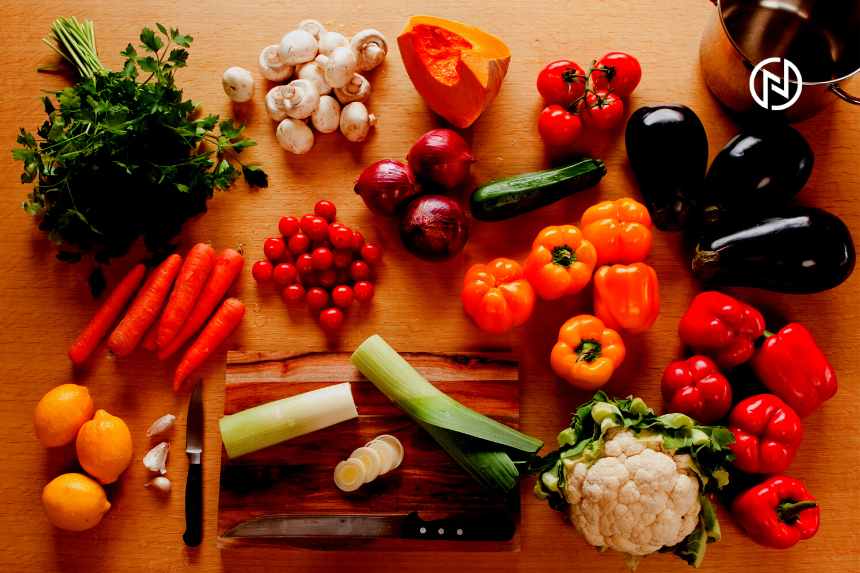
Vegetables
- Spinach: Loaded with iron, vitamins A and K, and antioxidants.
- Broccoli: Excellent source of vitamin C, fiber, and folate.
- Kale: High in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as calcium and iron.
- Carrots: Rich in vitamin A, fiber, and antioxidants.

Fruits
- Apples: High in fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants.
- Bananas: Good source of potassium, vitamin B6, and dietary fiber.
- Oranges: Rich in vitamin C, folate, and antioxidants.
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries): Packed with antioxidants, fiber, and vitamins.

Remember to check serving sizes and prepare foods in a variety of ways to maximize their nutritional benefits. These are just a few examples, and there are many more vegetarian foods available that can contribute to a healthy and balanced diet.
Please note that the nutritional values may vary slightly depending on the specific brand and preparation method, so it’s always a good idea to refer to food labels and consult with a registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice.













